Comparison Sorting Algorithms
/ Back / Home /
Comparison sorting is a class of sorting algorithms that relies on comparison operations (e.g. three way comparison ) to determine the order of two items in a set. In essence, these algorithms return a permutation of the original set so that the elements are ordered:
- Input: a set of n-items: \(a_1, a_2, a_3, ... , a_n\)
- Output: a permutation: \(a_{1}^{`}, a_{2}^{`}, a_{3}^{`}, ... , a_{n}^{`}\) such that \(a_{1}^{`} \leq a_{2}^{`} \leq a_{3}^{`}\leq ... \leq a_{n}^{`}\)
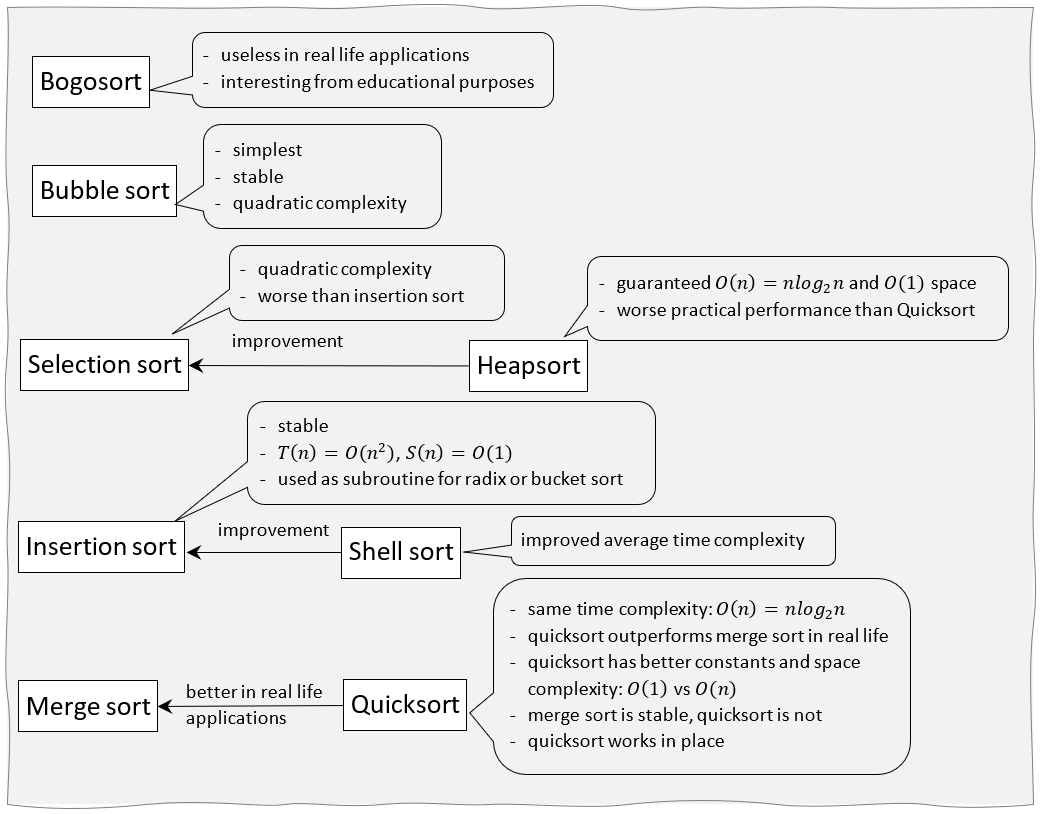
- Bogosort (aka. Shotgun sort, Stupid sort, Random sort, Permutation sort)
- Bubble Sort
- Selection Sort
- Insertion Sort
- Merge Sort
- Quicksort
- Heapsort
Complexity Table:
| Algorithm | T worst case | T avg case | T best case | Space aux. | Stable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bogosort | \(O(\infty)\) | \(O((n+1)!)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) | no |
| Bubble sort | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) | yes |
| Selection sort | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(1)\) | no |
| Insertion sort | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n)\) | \(O(1)\) | yes |
| Merge sort | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n)\) | yes |
| Quicksort | \(O(n^2)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n)\) | no |
| Heapsort | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(n \cdot log_{2}n)\) | \(O(1)\) | no |
Table legend: the first 3 columns contain the time complexity in the worst, average and best cases, column 4 the auxiliary space complexity, and column 5 the stability of the algorithm.
Note: Stability means that 2 equal keys keep relative order after sorting (eg 5 4 4’ 2 => 2 4 4’ 5: 4’ comes after 4 before and after sorting).
Quick view:
/ Back / Home /