Algorithm
Breadth First Search (BFS) finds all shortest paths from a given node (called the source) to all reachable nodes from it in an unweighted graph/digraph. We already went through BFS’s details in the Graph Traversal (TODO – add link) section so, here I’ll handle only the shortest paths property.
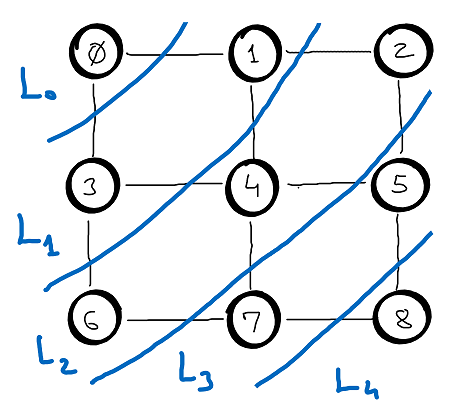
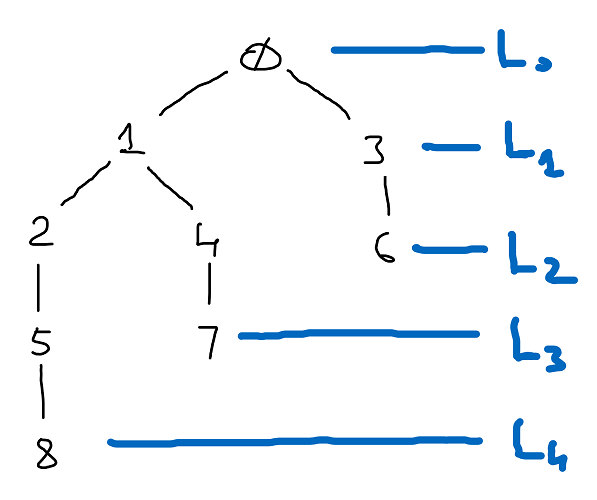
Claim: BFS computes the sets \(L_i\) of nodes at distance \(i\) from source \(s\) for all \(i\): \(L_i = \left \{ u : d(s, u) = i \right \}\).
Proof by induction:
Base case: \(u = s \Rightarrow d(s) = 0\), so \(s \in L_0\).
Inductive step: assume that the claim holds for all \(j \leq i\) and prove for \(i + 1\).
Consider the edge \((u, v)\), where \(u \in L_i\) and \(v \not \in L_i\).
So, when this edge is traversed, we have: \(d(s, v) \leq d(s, u) + 1\).
Since \(u \in L_i\) then \(d(s, u) = I\), so \(d(s, v) \leq i + 1\). (1)
However, since \(v \not \in L_j\) for any \(j \leq i\) by inductive hypothesis \(d(s, v) > i\). (2)
So, from (1) and (2) \(\Rightarrow d(s, v) = i + 1 \Rightarrow v \in L_{i+1}\).
Implementation
vector<int>
bfs(int start, int n, vector<vector<int>>& adjL) {
vector<int> dist(n, -1);
queue<int> q;
dist[start] = 0;
q.push(start);
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int v : adjL[u]) {
if (dist[v] == -1) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dist;
}
Example